Restoration
1660
Charles II restored to English throne
Created by Stacey Kikendall on Sun, 02/07/2021 - 17:58
This timeline presents important dates and events from the Restoration up through the end of the Victorian period, with special reference to authors and their works we read in class.
Charles II restored to English throne
Requires all officeholders to swear allegiance to Anglicanism
Charles II dissolves Parliament
James II was Charles II's Catholic brother
James II exiled and succeeded by his Protestant daughter, Mary, and her husband William of Orange
Written by John Locke
Written by John Locke
Written by Mary Astell
Anne was the other Protestant daughter of James II
Written by Mary Astell
Scotland becomes part of Great Britain
George I was the great-grandson of James I. He is the first Hanoverian king. Tory government replaced by Whigs.
Lady Mary Wortley Montagu writes her letters from Turkey
Written by Alexander Pope - final version
George II was George I's son.
Written by Jonathan Swift
Pained by William Hogarth
Charles Edward Stuart ("Bonnie Prince Charlie)'s defeat at Culloden ends the last Jacobite rebellion
Written by Samuel Johnson
George II dies, his son take the throne
Written by Anna Letitia Barbauld around 1771, published in 1773
American colonies rebel against British rule
 In 1781, passage of what is commonly known as the Sunday Observance Law. Discussion of the bill in the House of Commons started on May 3, 1781. Image: The Rt. Revd. Beilby Porteus, Bishop of London, printed by Fisher, Son & Co., London, 1833. Print of engraving by H. Meyer after J. Hoppner R. A.. This is a faithful photographic reproduction of an original two-dimensional work of art, and, so, is public domain, following U.S. case of Bridgeman v. Corel (1999).
In 1781, passage of what is commonly known as the Sunday Observance Law. Discussion of the bill in the House of Commons started on May 3, 1781. Image: The Rt. Revd. Beilby Porteus, Bishop of London, printed by Fisher, Son & Co., London, 1833. Print of engraving by H. Meyer after J. Hoppner R. A.. This is a faithful photographic reproduction of an original two-dimensional work of art, and, so, is public domain, following U.S. case of Bridgeman v. Corel (1999).
Passage of this Act, formally titled “Act for Preventing Certain Abuses and Profanations on the Lord’s Day, Called Sunday,” had a powerful, repressive effect on British society and culture for more than a century-and-a-half, as noted by both its proponent (Bishop Beilby Porteus) and its many Victorian critics, among them John Stuart Mill in On Liberty.
Christopher Lane, "On the Victorian Afterlife of the 1781 Sunday Observance Act"
 On 9 April 1787, 451 people set sail to establish a “Province of Freedom” in Africa, later to become Sierra Leone. Image: An illustration of liberated slaves arriving in Sierra Leone, from the 1835 book, A System of School Geography Chiefly Derived from Malte-Brun, by Samuel Griswold Goodrich. This image is in the public domain in the United States as its copyright has expired.
On 9 April 1787, 451 people set sail to establish a “Province of Freedom” in Africa, later to become Sierra Leone. Image: An illustration of liberated slaves arriving in Sierra Leone, from the 1835 book, A System of School Geography Chiefly Derived from Malte-Brun, by Samuel Griswold Goodrich. This image is in the public domain in the United States as its copyright has expired.
Isaac Land, “On the Foundings of Sierra Leone, 1787-1808″
Written by Charlotte Smith, included in her collection Elegiac Sonnets
 1789 saw the publication of Olaudah Equiano’s Interesting Narrative of the Life of Olaudah Equiano, Or Gustavus Vassa, The African. Exact month of publication unknown; if you have information about the correct date, please email felluga@purdue.edu with this information. The book describes Equiano's time as a slave and his life after achieving his freedom. Image: Engraving for Equiano's Interesting Narrative. This image is in the public domain in the United States as its copyright has expired.
1789 saw the publication of Olaudah Equiano’s Interesting Narrative of the Life of Olaudah Equiano, Or Gustavus Vassa, The African. Exact month of publication unknown; if you have information about the correct date, please email felluga@purdue.edu with this information. The book describes Equiano's time as a slave and his life after achieving his freedom. Image: Engraving for Equiano's Interesting Narrative. This image is in the public domain in the United States as its copyright has expired.
Isaac Land, “On the Foundings of Sierra Leone, 1787-1808″
 The French Revolution occurred from 5 May 1789 to 9-10 November 1799. Image: Jean-Jacques-François Le Barbier, Representation of The Declaration of the Rights of Man and of the Citizen of 26 August 1789 (c. 1789). This work is in the public domain in the United States.
The French Revolution occurred from 5 May 1789 to 9-10 November 1799. Image: Jean-Jacques-François Le Barbier, Representation of The Declaration of the Rights of Man and of the Citizen of 26 August 1789 (c. 1789). This work is in the public domain in the United States.
On 5 May 1789, the Estates-General, representing the nobility, the clergy, and the common people, held a meeting at the request of the King to address France’s financial difficulties. At this meeting, the Third Estate (the commoners) protested the merely symbolic double representation that they had been granted by the King. This protest resulted in a fracture among the three estates and precipitated the French Revolution. On 17 June, members of the Third Estate designated themselves the National Assembly and claimed to represent the people of the nation, thus preparing the way for the foundation of the republic. Several pivotal events followed in quick succession: the storming of the Bastille (14 July), the approval of the Declaration of the Rights of Man and of the Citizen (26 August), and the march on Versailles that led to the enforced relocation of the royal family to Paris (5-6 October). These revolutionary acts fired the imagination of many regarding the political future of France, and, indeed, all of Europe. The republican period of the revolution continued in various phases until 9-10 November 1799 when Napoleon Bonaparte supplanted the government.
Diane Piccitto, "On 1793 and the Aftermath of the French Revolution"
Written by Anna Letitia Barbauld
 In January 1792, Mary Wollstonecraft published A Vindication of the Rights of Woman, which laid out the tenets of what today we call ‘equality’ or ‘liberal’ feminist theory. She further promoted a new model of the nation grounded on a family politics produced by egalitarian marriages. Image: A Vindication of the Rights of Woman title page from the first American edition, 1792 (Library of Congress). This image is in the public domain in the United States because its copyright has expired.
In January 1792, Mary Wollstonecraft published A Vindication of the Rights of Woman, which laid out the tenets of what today we call ‘equality’ or ‘liberal’ feminist theory. She further promoted a new model of the nation grounded on a family politics produced by egalitarian marriages. Image: A Vindication of the Rights of Woman title page from the first American edition, 1792 (Library of Congress). This image is in the public domain in the United States because its copyright has expired.
Anne K. Mellor, "On the Publication of A Vindication of the Rights of Woman"
 A period of violence that occurred a few years after the start of the French Revolution. Image: Anonymous, Portrait of Maximilien de Robespierre (c. 1790), Carnavalet Museum. This image is in the public domain in the United States because its copyright has expired.
A period of violence that occurred a few years after the start of the French Revolution. Image: Anonymous, Portrait of Maximilien de Robespierre (c. 1790), Carnavalet Museum. This image is in the public domain in the United States because its copyright has expired.
On 5 September 1793, the National Convention, France’s ruling body from 1793 to 1795, officially put into effect terror measures in order to subdue opposition to and punish insufficient support for the revolution and the new regime. From the autumn of 1793 until the summer of 1794, thousands of people across the country were imprisoned and executed (including the Queen) under the ruthless leadership of Maximilien Robespierre. The guillotine, particularly the one in Paris’s Place de la Révolution, served as the bloody emblem of the fear tactics that began to manifest themselves first in the formation of the Committee of Public Safety (6 April 1793) and subsequently in the implementation of the Law of Suspects (17 September 1793). The Terror ended on 27 July 1794 with the overthrow of Robespierre, who was guillotined the next day.
Diane Piccitto, "On 1793 and the Aftermath of the French Revolution"
Written by William Blake
The Songs of Innocence was originally etched in 1789, but was combined with additional poems in 1794 as Songs of Innocence and of Experience
Uprising against British rule in Ireland, had help of French but were eventually defeated
Parliamentary Union of Ireland and Great Britain. Act of Union passed in 1800, took effect in 1801
 In 1801, the Consolidation (Inclosure Act) was passed: Parliament thus formalized procedures for enclosing common land, removing previously existing rights of the people to carry out certain activities in these "common" lands. Exact month of passing unknown; if you have information about the correct date, please email felluga@purdue.edu with this information. Image: Detail from Peter Paul Rubens, A View of Het Steen in the Early Morning, c. 1636 (National Gallery, London), illustrating a pre-Enclosure landscape. This image is in the public domain in the United States because its copyright has expired.
In 1801, the Consolidation (Inclosure Act) was passed: Parliament thus formalized procedures for enclosing common land, removing previously existing rights of the people to carry out certain activities in these "common" lands. Exact month of passing unknown; if you have information about the correct date, please email felluga@purdue.edu with this information. Image: Detail from Peter Paul Rubens, A View of Het Steen in the Early Morning, c. 1636 (National Gallery, London), illustrating a pre-Enclosure landscape. This image is in the public domain in the United States because its copyright has expired.
Carolyn Lesjak, "1750 to the Present: Acts of Enclosure and Their Afterlife" (forthcoming)
Ellen Rosenman, “On Enclosure Acts and the Commons”
William Wordsworth's Lyrical Ballads, 3rd edition, containing the expanded and final version of the famous "Preface," one of the founding theoretical statements of the Romantic poetical movement.
This image is in the public domain in the United States because its copyright is expired. www.abebooks.com/first-edition…...
Jules Law, “Victorian Virtual Reality”
 On 26 May 1805, Napoleon crowns himself King of Italy in Milan Cathedral, with the iron crown of Lombardy. Image: The Iron Crown of Lombardy, from Cesare Cantù Grande illustrazione del Lombardo-Veneto ossia storia delle città, dei borghi, comuni, castelli, ecc. fino ai tempi moderni Milano, Corona e Caimi Editori, 1858. This image is in the public domain in the United States because its copyright has expired.
On 26 May 1805, Napoleon crowns himself King of Italy in Milan Cathedral, with the iron crown of Lombardy. Image: The Iron Crown of Lombardy, from Cesare Cantù Grande illustrazione del Lombardo-Veneto ossia storia delle città, dei borghi, comuni, castelli, ecc. fino ai tempi moderni Milano, Corona e Caimi Editori, 1858. This image is in the public domain in the United States because its copyright has expired.
In a flamboyant and highly theatrical gesture, Napoleon Bonaparte signifies his political and military dominance over the Italian peninsula with a ceremony in Milan Cathedral, where he crowned himself King of Italy with the ancient, iconic iron crown of Lombardy. This crowning of Napoleon as King is a result of the French conquest of Italy. His full title was "Emperor of the French and King of Italy."
Alison Chapman, "On Il Risorgimento"
Erik Simpson, “On Corinne, Or Italy”
Slave trade outlawed (but not slavery itself)
George, Prince of Wales, acts as regent for George III, who has been declared incurably insane
On 16 October 1811, the National Society for the Education of Poor Children in the Principles of the Established Church (the Church of England) was founded to establish “National Schools.” According to their founders, poor children were to be taught to avoid vice and behave in an orderly manner within their station. To limit costs, the monitorial system was employed, by which more advanced pupils taught younger ones.
Florence S. Boos, “The Education Act of 1870: Before and After”
War between Britain and United States
Written by Jane Austen
Napoleon was exiled to Elba, an island in the Meditteranean, after he abdicated on 6 April 1814. He spent nine months and 21 days on the island, then attempted to retake his empire, leaving the island on 26 February 1815. Napoleon was definitively defeated at the Battle of Waterloo on 18 June 1815.
 On 23 March 1815, parliament passed the Corn Law Act of 1815. Image: the Royal coat of arms of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland.
On 23 March 1815, parliament passed the Corn Law Act of 1815. Image: the Royal coat of arms of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland.
The Corn Law Act of 1815 prohibited the importation of grain when the prices in the domestic market were high. The Act was repealed on 25 June 1846.
Ayse Çelikkol, "On the Repeal of the Corn Laws, 1846"
 Dec 1815 publication of Jane Austen's Emma. Austen's fourth published novel, Emma, was in press when the Prince Regent sent word that she had his permission to dedicate this or any later work to him, a permission of which she never availed herself. Image: Title page from Jane Austen's first edition of Emma, 1816 (Lilly Library, Indiana U). This image is in the public domain in the United States because its copyright has expired.
Dec 1815 publication of Jane Austen's Emma. Austen's fourth published novel, Emma, was in press when the Prince Regent sent word that she had his permission to dedicate this or any later work to him, a permission of which she never availed herself. Image: Title page from Jane Austen's first edition of Emma, 1816 (Lilly Library, Indiana U). This image is in the public domain in the United States because its copyright has expired.
Anne Wallace, “On the Deceased Wife’s Sister Controversy, 1835-1907″
 On 1 April 1817, the first number of Blackwood’s Edinburgh Magazine was published. Founded by Scottish bookseller and publisher William Blackwood, the monthly literary magazine targeted a growing middle-class readership. Image: Paper cover for issue of Blackwood’s Edinburgh Magazine (Nov. 1866). This image is in the public domain in the United States as its copyright has expired.
On 1 April 1817, the first number of Blackwood’s Edinburgh Magazine was published. Founded by Scottish bookseller and publisher William Blackwood, the monthly literary magazine targeted a growing middle-class readership. Image: Paper cover for issue of Blackwood’s Edinburgh Magazine (Nov. 1866). This image is in the public domain in the United States as its copyright has expired.
Michelle Allen-Emerson, “On Magazine Day”
Ina Ferris, “The Debut of The Edinburgh Review, 1802″
 On Saturday, 26 September 1818, James Blundell conducted the first medical blood transfusion between human subjects. During the course of the century, transfusion was applied as a remedy to different kinds of sicknesses and injuries, and performed at different times with various fluids. Image: James Blundell’s Gravitator, from “Observations on the Transfusion of Blood, with a Description of his Gravitator.” This image is in the public domain in the United States as its copyright has expired.
On Saturday, 26 September 1818, James Blundell conducted the first medical blood transfusion between human subjects. During the course of the century, transfusion was applied as a remedy to different kinds of sicknesses and injuries, and performed at different times with various fluids. Image: James Blundell’s Gravitator, from “Observations on the Transfusion of Blood, with a Description of his Gravitator.” This image is in the public domain in the United States as its copyright has expired.
Matthew Rowlinson, “On the First Medical Blood Transfusion Between Human Subjects, 1818″
On 12 July 1819, the British government approved £50,000 for a settlement scheme to South Africa's eastern Cape.
Timothy Johns, “The 1820 Settlement Scheme to South Africa”
 On 16 August 1819, at St. Peter’s Field, Manchester, more than 60,000 workers gathered to demonstrate in favor of an expansion of suffrage in England. In an attempt to disperse the crowd and arrest the organizers of the demonstration, local cavalry and members of the 15th Hussars and 88th Foot attacked the crowd, killing a dozen protestors and injuring as many as 600. Though Wellington was not involved, the incident was dubbed “Peterloo” because of his persistent opposition to reform in the House of Lords. Image: Richard Carlisle, To Henry Hunt, Esq., as chairman of the emeeting assembled in St. Peter's Field, Manchester, sixteenth day of August, 1819, and to the female Reformers of Manchester and the adjacent towns who were exposed to and suffered from the wanton and fiendish attack made on them by that brutal armed force, the Manchester and Cheshire Yeomanry Cavalry, this plate is dedicated by their fellow labourer, Richard Carlile: a coloured engraving that depicts the Peterloo Massacre (1 October 1819), Manchester Library Services. This image is in the public domain in the United States because its copyright has expired.
On 16 August 1819, at St. Peter’s Field, Manchester, more than 60,000 workers gathered to demonstrate in favor of an expansion of suffrage in England. In an attempt to disperse the crowd and arrest the organizers of the demonstration, local cavalry and members of the 15th Hussars and 88th Foot attacked the crowd, killing a dozen protestors and injuring as many as 600. Though Wellington was not involved, the incident was dubbed “Peterloo” because of his persistent opposition to reform in the House of Lords. Image: Richard Carlisle, To Henry Hunt, Esq., as chairman of the emeeting assembled in St. Peter's Field, Manchester, sixteenth day of August, 1819, and to the female Reformers of Manchester and the adjacent towns who were exposed to and suffered from the wanton and fiendish attack made on them by that brutal armed force, the Manchester and Cheshire Yeomanry Cavalry, this plate is dedicated by their fellow labourer, Richard Carlile: a coloured engraving that depicts the Peterloo Massacre (1 October 1819), Manchester Library Services. This image is in the public domain in the United States because its copyright has expired.
James Chandler, “On Peterloo, 16 August 1819″
Sean Grass, “On the Death of the Duke of Wellington, 14 September 1852″
On 1 November 1819, simultaneous meetings were held, by prior agreement, at Newcastle, Carlisle, Leeds Halifax, Manchester, Bolton, Nottingham, Leicester, Coventry, and elsewhere in England and Scotland.
James Chandler, “On Peterloo, 16 August 1819″
On 15 November 1819, simultaneous radical meetings occurred at Paisley, Glasgow, and other locations across Scotland.
James Chandler, “On Peterloo, 16 August 1819″
 On 30 December 1819, the British parliament passed the Six Acts (or Gag Acts), which labeled any meeting for radical reform as “an overt act of treasonable conspiracy.” The acts were aimed at gagging radical newspapers (the Blasphemous and Seditious Libels Act, the Newspaper and Stamp Duties Act, and the Misdemeanors Act), preventing large meetings (the Seditious Meetings Prevention Act), and reducing what the government saw as the possibility of armed insurrection (the Training Prevention Act and the Seizure of Arms Act). Image: The Royal coat of arms of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland.
On 30 December 1819, the British parliament passed the Six Acts (or Gag Acts), which labeled any meeting for radical reform as “an overt act of treasonable conspiracy.” The acts were aimed at gagging radical newspapers (the Blasphemous and Seditious Libels Act, the Newspaper and Stamp Duties Act, and the Misdemeanors Act), preventing large meetings (the Seditious Meetings Prevention Act), and reducing what the government saw as the possibility of armed insurrection (the Training Prevention Act and the Seizure of Arms Act). Image: The Royal coat of arms of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland.
James Chandler, “On Peterloo, 16 August 1819″
Written by John Keats
After serving as Regent for years, he eventually becomes King when his father dies.
Napoleon Bonaparte died on 5 May 1821 while in Exile on the island of Saint Helena. Image: Horace Vernet, Napoleon on his Death Bed (1826).
On 16 June 1824, founding of the Society for the Protection of Animals (SPCA) in London. The Society became the Royal Society in 1840, when it was granted a royal charter by Queen Victoria, herself strongly opposed to vivisection.
Susan Hamilton (U Alberta), “On the Cruelty to Animals Act, 15 August 1876″
Philip Howell, “June 1859/December 1860: The Dog Show and the Dogs’ Home”
Mario Ortiz-Robles, “Animal Acts: 1822, 1835, 1849, 1850, 1854, 1876, 1900″
On April 1825, the British stock market began to crash. After the speculative bubble reached its peak, falling Bank of England gold reserves and a collapse in stock prices lead to panic by the end of the year.
Angela Esterhammer, “1824: Improvisation, Speculation, and Identity-Construction”
 On December 1825, bank failures began in London. The collapse of important City banks lead to further bank failures across Britain and brought financial crisis to the point where the Bank of England must take extreme measures. Image: The main Bank of England façade, c. 1980. Permission is granted to copy, distribute and/or modify this document under the terms of the GNU Free Documentation License, Version 1.2 or any later version published by the Free Software Foundation.
On December 1825, bank failures began in London. The collapse of important City banks lead to further bank failures across Britain and brought financial crisis to the point where the Bank of England must take extreme measures. Image: The main Bank of England façade, c. 1980. Permission is granted to copy, distribute and/or modify this document under the terms of the GNU Free Documentation License, Version 1.2 or any later version published by the Free Software Foundation.
Alexander J. Dick, “On the Financial Crisis, 1825-26″
Angela Esterhammer, “1824: Improvisation, Speculation, and Identity-Construction”
Lana L. Dalley, “On Martineau’s Illustrations of Political Economy, 1832-34″
Parliamentary repeal of the Test and Corporation Acts excluding Dissenters from state offices
 Roman Catholic Relief Act received the Royal Assent on 13 April 1829 (sometimes called the Catholic Emancipation Act). Image: the Royal coat of arms of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland.
Roman Catholic Relief Act received the Royal Assent on 13 April 1829 (sometimes called the Catholic Emancipation Act). Image: the Royal coat of arms of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland.
The Catholic Relief Act of 1829 allowed Catholics to become Members of Parliament and to hold public offices, but it also raised the property qualifications that allowed individuals in Ireland to vote. The passage of the Catholic Relief Act marked a shift in English political power from the House of Lords to the House of Commons. The Act was led by the Duke of Wellington and passed despite initially serious opposition from both the House of Lords and King George IV.
Carolyn Vellenga Berman, “On the Reform Act of 1832″
Sean Grass, “On the Death of the Duke of Wellington, 14 September 1852″
Brother of George IV, son of George III
 January 1830 saw the publication of the first volume (of three) of Charles Lyell’s Principles of Geology (January 1830). Image: G. J. Stodart (engraver), Portrait of Charles Lyell (unknown date).
January 1830 saw the publication of the first volume (of three) of Charles Lyell’s Principles of Geology (January 1830). Image: G. J. Stodart (engraver), Portrait of Charles Lyell (unknown date).
Lyell’s work, though contested, establishes the preeminence of Uniformitarian principles in the interpretation of Geological phenomena, and allows vast temporal scope for Charles Darwin’s subsequent model of evolutionary development.
Martin Meisel, "On the Age of the Universe"
Nancy Armstrong, “On Charles Darwin’s The Descent of Man, 24 February 1871″
Ian Duncan, “On Charles Darwin and the Voyage of the Beagle”
Anna Henchman, “Charles Darwin’s Final Book on Earthworms, 1881”
Cannon Schmitt, “On the Publication of Charles Darwin’s On the Origin of Species, 1859″
 On 26 June 1830, King George IV died, prompting a dissolution of Parliament which brought the Whigs to power in a coalition government; he was succeeded by King William IV. Image: 1798 Engraving of King George IV (by Salomon Jomtob Bennett, after Sir William Beechey). This image is in the public domain in the United States because its copyright has expired.
On 26 June 1830, King George IV died, prompting a dissolution of Parliament which brought the Whigs to power in a coalition government; he was succeeded by King William IV. Image: 1798 Engraving of King George IV (by Salomon Jomtob Bennett, after Sir William Beechey). This image is in the public domain in the United States because its copyright has expired.
Carolyn Vellenga Berman, “On the Reform Act of 1832″
 The Swing Riots, which occurred from August 1830 to December 1830, were a series of riots by agricultural workers that resulted from the Enclosure Acts, in general, and the introduction of threshing machines in East Kent, more specifically. The Swing Riots are named after the fictitious “Captain Swing,” the figurehead for the movement. Image: Print by Henry Heath entitled “Swing!” (1830). Reproduced with permission from The British Museum.
The Swing Riots, which occurred from August 1830 to December 1830, were a series of riots by agricultural workers that resulted from the Enclosure Acts, in general, and the introduction of threshing machines in East Kent, more specifically. The Swing Riots are named after the fictitious “Captain Swing,” the figurehead for the movement. Image: Print by Henry Heath entitled “Swing!” (1830). Reproduced with permission from The British Museum.
Carolyn Lesjak, "1750 to the Present: Acts of Enclosure and Their Afterlife" (forthcoming)
 On 15 September 1830, the world’s first major passenger railway opened with a huge celebration—and an unforgettable tragedy. The Liverpool and Manchester Railway stages a grand public opening with dignitaries including then-prime-minster Duke of Wellington. But, before the inaugural trains reach their destination, a fatal accident occurs to MP William Huskisson and, in Manchester, the cheering crowds give way to angry political protests. Image: The Remains of Stephenson's 'Rocket', 1829. Used with permission. Copyright (c) National Railway Museum / Science & Society Picture Library.
On 15 September 1830, the world’s first major passenger railway opened with a huge celebration—and an unforgettable tragedy. The Liverpool and Manchester Railway stages a grand public opening with dignitaries including then-prime-minster Duke of Wellington. But, before the inaugural trains reach their destination, a fatal accident occurs to MP William Huskisson and, in Manchester, the cheering crowds give way to angry political protests. Image: The Remains of Stephenson's 'Rocket', 1829. Used with permission. Copyright (c) National Railway Museum / Science & Society Picture Library.
Paul Fyfe, “On the Opening of the Liverpool and Manchester Railway, 1830″
Story by Mary Prince, transcribed by Suzanna Strickland, edited by Thomas Pringle
The first major cholera pandemic to cross the Channel began in Sunderland in September 1831, spread throughout the country, and was not determined to be over until more than a year later, in December of 1832.
Pamela Gilbert, "On Cholera in Nineteenth-Century England"
 From October 1831 to October 1836, Charles Darwin circumnavigated the world as ship’s naturalist on board the H.M.S. Beagle; he later published his first book based on the journal of his experiences and observations during the voyage. Image: Henry Maull and John Fox, Photograph of Charles Darwin (c. 1854). This image is in the public domain in the United States because its copyright has expired.
From October 1831 to October 1836, Charles Darwin circumnavigated the world as ship’s naturalist on board the H.M.S. Beagle; he later published his first book based on the journal of his experiences and observations during the voyage. Image: Henry Maull and John Fox, Photograph of Charles Darwin (c. 1854). This image is in the public domain in the United States because its copyright has expired.
Nancy Armstrong, “On Charles Darwin’s The Descent of Man, 24 February 1871″
Ian Duncan, “On Charles Darwin and the Voyage of the Beagle”
Anna Henchman, “Charles Darwin’s Final Book on Earthworms, 1881”
Cannon Schmitt, “On the Publication of Charles Darwin’s On the Origin of Species, 1859″
Daniel Bivona, “On W. K. Clifford and ‘The Ethics of Belief,’ 11 April 1876″
 The Slavery Abolition Act of 1833 received the Royal Assent (which means it became law) on 29 August 1833. The Act outlawed slavery throughout the British Empire; Britain’s colonial slaves were officially emancipated on 1 August 1834 when the law came into force, although most entered a form of obligatory apprenticeship that ended in 1840. Image: The Royal coat of arms of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland. Image: the Royal coat of arms of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland.
The Slavery Abolition Act of 1833 received the Royal Assent (which means it became law) on 29 August 1833. The Act outlawed slavery throughout the British Empire; Britain’s colonial slaves were officially emancipated on 1 August 1834 when the law came into force, although most entered a form of obligatory apprenticeship that ended in 1840. Image: The Royal coat of arms of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland. Image: the Royal coat of arms of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland.
 Act to Regulate the Labour of Children and Young Persons in the Mills and Factories of the United Kingdom passed on 29 August 1833. Image: the Royal coat of arms of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland.
Act to Regulate the Labour of Children and Young Persons in the Mills and Factories of the United Kingdom passed on 29 August 1833. Image: the Royal coat of arms of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland.
Peter Capuano, “On Sir Charles Bell’s The Hand, 1833″
On 28 May 1836, Elizabeth Barrett Browning met William Wordsworth at a literary dinner in London; EBB's cousin, John Kenyon, was the host and the event most likely occurred at Kenyon's main residence at the time: 39 Devonshire Place, London, which is right around the corner from EBB's residence at the time: 50 Wimpole Street. See the associated map.
 On 13 August 1836, the Newspaper Act was passed, an Act to Consolidate and Amend the Laws relating to the Conveyance of Newspapers by the Post. The bill reduced the stamp duty on newspapers to 1d, thus allowing the channels for communication to increase dramatically. Image: The Royal coat of arms of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland.
On 13 August 1836, the Newspaper Act was passed, an Act to Consolidate and Amend the Laws relating to the Conveyance of Newspapers by the Post. The bill reduced the stamp duty on newspapers to 1d, thus allowing the channels for communication to increase dramatically. Image: The Royal coat of arms of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland.
Elaine Hadley, “On Opinion Politics and the Ballot Act of 1872″
 From February 1837 to April 1839, Charles Dickens published Oliver Twist. Image: Photograph of Charles Dickens by Jeremiah Gurney, c. 1867-1868 (at the Heritage Auction Gallery). This image is in the public domain in the United States as its copyright has expired.
From February 1837 to April 1839, Charles Dickens published Oliver Twist. Image: Photograph of Charles Dickens by Jeremiah Gurney, c. 1867-1868 (at the Heritage Auction Gallery). This image is in the public domain in the United States as its copyright has expired.
Heidi Kaufman, “1800-1900: Inside and Outside the Nineteenth-Century East End”
Michelle Allen-Emerson, “On Magazine Day”
 On 17 August 1839, passage of an Act to Amend the Law Relating to the Custody of Infants. The Act allowed a separated wife to petition the court for custody of her children under the age of seven. Image: The Royal coat of arms of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland.
On 17 August 1839, passage of an Act to Amend the Law Relating to the Custody of Infants. The Act allowed a separated wife to petition the court for custody of her children under the age of seven. Image: The Royal coat of arms of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland.
Rachel Ablow, “‘One Flesh,’ One Person, and the 1870 Married Women’s Property Act”
Kelly Hager, “Chipping Away at Coverture: The Matrimonial Causes Act of 1857″
Jill Rappoport, “Wives and Sons: Coverture, Primogeniture, and Married Women’s Property”
With a fellow reformer, E. Carleton Tuftnell, Kay-Shuttleworth established in February 1840 the first pupil-teacher training school in Battersea. This system was later extended to schools administered by the National and British Societies.
Florence S. Boos, “The Education Act of 1870: Before and After”
On July 17 1841, Punch, a mass-circulation periodical, was launched.
 On May 14 1842, The Illustrated London News, a mass-circulation periodical, was launched. Image: Masthead of the Illustrated London News. This image is in the public domain in the United States because its copyright has expired.
On May 14 1842, The Illustrated London News, a mass-circulation periodical, was launched. Image: Masthead of the Illustrated London News. This image is in the public domain in the United States because its copyright has expired.
 In September 1848, the Pre-Raphaelite Brotherhood was founded by William Holman Hunt, John Everett Millais and Dante Gabriel Rossetti. The brotherhood reacts, in part, against the use of bitumen, a transparent brown used for depicting exaggerated shadows, aiming instead to reproduce the sharp, brilliant colors found in fifteenth-century art. Image: Portrait of Dante Gabriel Rossetti: albumen print. This photograph, from 7 October 1863, was reproduced as the frontispiece of: Rossetti, William Michael, Dante Gabriel Rossetti as Designer and Writer. London: Cassell and Company, 1898.
In September 1848, the Pre-Raphaelite Brotherhood was founded by William Holman Hunt, John Everett Millais and Dante Gabriel Rossetti. The brotherhood reacts, in part, against the use of bitumen, a transparent brown used for depicting exaggerated shadows, aiming instead to reproduce the sharp, brilliant colors found in fifteenth-century art. Image: Portrait of Dante Gabriel Rossetti: albumen print. This photograph, from 7 October 1863, was reproduced as the frontispiece of: Rossetti, William Michael, Dante Gabriel Rossetti as Designer and Writer. London: Cassell and Company, 1898.
Elizabeth Helsinger, “Lyric Poetry and the Event of Poems, 1870″
Morna O’Neill, “On Walter Crane and the Aims of Decorative Art”
Linda M. Shires, "On Color Theory, 1835: George Field’s Chromatography"
The second major cholera epidemic in the UK began in Scotland in October 1848 and is generally agreed to have largely subsided in the UK by the end of 1849.
Pamela Gilbert, "On Cholera in Nineteenth-Century England"
 In June 1850, publication of Alfred Tennyson’s In Memoriam A.H.H. Image: Julia Margaret Cameron, Carbon print of Alfred Lord Tennyson, 1869, printed 1875/79 (The Art Institute of Chicago). This image is in the public domain in the United States because its copyright has expired.
In June 1850, publication of Alfred Tennyson’s In Memoriam A.H.H. Image: Julia Margaret Cameron, Carbon print of Alfred Lord Tennyson, 1869, printed 1875/79 (The Art Institute of Chicago). This image is in the public domain in the United States because its copyright has expired.
On 29 September 1850, Pius IX restored England’s ecclesiastical hierarchy; the post-seventeenth-century system of Vicars Apostolic was replaced with a hierarchy in line with the system still in place in Ireland. This change contributed to the so-called Papal Aggression over the years 1850-52, a campaign against Roman Catholocism.
Miriam Burstein, “The ‘Papal Aggression’ Controversy, 1850-52″
Barbara Charlesworth Gelpi (Stanford), “14 July 1833: John Keble’s Assize Sermon, National Apostasy”
 1851 saw the publication of Henry Mayhew's London Labour and the London Poor. London Labour appeared as a series of articles in the Morning Chronicle throughout the 1840s, before being compiled into three volumes in 1851. Exact month of publication unknown; if you have information about the correct date, please email felluga@purdue.edu with this information. The articles were innovative in the way they articulated the voices of the poorer classes of London. As an ethnographic study, Mayhew’s work explores the multicultural textures of Britain’s center, drawing attention to the ethnic diversity within a nation determined to maintain a stable national and cultural identity. Image: Henry Mayhew, taken from the 1861 edition of London Labour and the London Poor. This image is in the public domain in the United States as its copyright has expired.
1851 saw the publication of Henry Mayhew's London Labour and the London Poor. London Labour appeared as a series of articles in the Morning Chronicle throughout the 1840s, before being compiled into three volumes in 1851. Exact month of publication unknown; if you have information about the correct date, please email felluga@purdue.edu with this information. The articles were innovative in the way they articulated the voices of the poorer classes of London. As an ethnographic study, Mayhew’s work explores the multicultural textures of Britain’s center, drawing attention to the ethnic diversity within a nation determined to maintain a stable national and cultural identity. Image: Henry Mayhew, taken from the 1861 edition of London Labour and the London Poor. This image is in the public domain in the United States as its copyright has expired.
Heidi Kaufman, “1800-1900: Inside and Outside the Nineteenth-Century East End”
ON 5 Sept 1852, the Manchester Public Library opened. This was Britain’s first free public lending library, opened under the 1850 Public Libraries Act.
Amy Woodson-Boulton, “The City Art Museum Movement and the Social Role of Art”
On 28 March 1854, Britain declares war against Russia, thus entering the Crimean War. Image: Russo-British skirmish during Crimean War (anonymous plate). This image is in the public domain in the United States because its copyright has expired.
In 1854, in defense of the Turks and of British access to eastern trade routes, Britain entered into war in the Crimea. The two-year campaign represented the nation’s first major military engagement since the end of the Napoleonic wars. It thus sheds light on mid-Victorian attitudes towards national identity, offering a counter-narrative to views of the 1850s dominated by responses to the Great Exhibition of 1851. As literary and visual representations of the war reveal, reactions to this conflict were both more nuanced and more ambivalent than our preconceptions about Victorian jingoism might anticipate.
Stefanie Markovits, "On the Crimean War and the Charge of the Light Brigade"
Opening of the Crystal Palace at Sydenham on 10 June 1854. Image: The Crystal Palace on fire (30 November 1936; author unknown). This image is in the public domain in the United States because its copyright has expired.
The resurrection of the Crystal Palace of 1851 in its new setting at Sydenham, with an expanded architectural complex and enhanced functional brief, embodies the Victorian emphasis upon visuality as a means of acquiring and conveying knowledge. In addition, the new Crystal Palace was shaped by prevailing concepts of rational recreation and beneficial commerce that insisted that private and public interests could be simultaneously satisfied and lead to a stronger nation and even Empire.
Anne Helmreich, "On the Opening of the Crystal Palace at Sydenham, 10 June 1854"
Audrey Jaffe, "On the Great Exhibition"
Aviva Briefel, "On the 1886 Colonial and Indian Exhibition"
Anne Clendinning, “On The British Empire Exhibition, 1924-25″
On 14 March 1856, presentation of the Petition for Reform of the Married Women’s Property Law, 1856. The petition began the joint effort by lawmakers and public women to grant married women control of their own wealth.
Jill Rappoport, “Wives and Sons: Coverture, Primogeniture, and Married Women’s Property”
Rachel Ablow, “‘One Flesh,’ One Person, and the 1870 Married Women’s Property Act”
Anne D. Wallace, “On the Deceased Wife’s Sister Controversy, 1835-1907″
On 30 March 1856, signing of the Treaty of Paris, ending the Crimean War. Image: Treaty of Paris, the participants (Contemporary woodcut, published in Magazin Istoric, 1856). This image is in the public domain in the United States because its copyright has expired.
Stefanie Markovits, "On the Crimean War and the Charge of the Light Brigade"
 On 15 November 1856, Elizabeth Barrett Browning’s Aurora Leigh was published by Chapman and Hall in Great Britain. Aurora Leigh—a verse-novel and modern epic—set off literary, social, and political reverberations in Britain, North America, and Europe up to the end of the century. Given its innovative, generically mixed form and its controversial contemporary subject matter, it figured in debates over poetry and poetics, the nature of the realist novel, class divisions and social reform, women’s rights, religion, and the politics of nations. Image: An 1871 engraving of an 1859 photograph of Elizabeth Barrett Browning (photograph by Macaire Havre, engraving by T. O. Barlow). This image is in the public domain in the United States because its copyright has expired.
On 15 November 1856, Elizabeth Barrett Browning’s Aurora Leigh was published by Chapman and Hall in Great Britain. Aurora Leigh—a verse-novel and modern epic—set off literary, social, and political reverberations in Britain, North America, and Europe up to the end of the century. Given its innovative, generically mixed form and its controversial contemporary subject matter, it figured in debates over poetry and poetics, the nature of the realist novel, class divisions and social reform, women’s rights, religion, and the politics of nations. Image: An 1871 engraving of an 1859 photograph of Elizabeth Barrett Browning (photograph by Macaire Havre, engraving by T. O. Barlow). This image is in the public domain in the United States because its copyright has expired.
Marjorie Stone, “The ‘Advent’ of Aurora Leigh: Critical Myths and Periodical Debates”
 The Indian Rebellion or Uprising, also known as the Sepoy Mutiny, began as a mutiny of sepoys of the British East India Company's army on 10 May 1857, in the town of Meerut, and soon escalated into other mutinies and civilian rebellions. It was not contained until the fall of Gwalior on 20 June 1858. Image: Felice Beato, Print of the hanging of two rebels, 1858 (albumen silver print). This image is in the public domain in the United States because its copyright has expired.
The Indian Rebellion or Uprising, also known as the Sepoy Mutiny, began as a mutiny of sepoys of the British East India Company's army on 10 May 1857, in the town of Meerut, and soon escalated into other mutinies and civilian rebellions. It was not contained until the fall of Gwalior on 20 June 1858. Image: Felice Beato, Print of the hanging of two rebels, 1858 (albumen silver print). This image is in the public domain in the United States because its copyright has expired.
Priti Joshi, “1857; or, Can the Indian ‘Mutiny’ Be Fixed?”
Julie Codell, “On the Delhi Coronation Durbars, 1877, 1903, 1911″
 Pre-Raphaelite Art Exhibit, Russell Square, London, from 25 May to 25 June 1857. This was the first exhibition devoted solely to the work of the Pre-Raphaelites. Image: Portrait of Dante Gabriel Rossetti: albumen print. This photograph, from 7 October 1863, was reproduced as the frontispiece of: Rossetti, William Michael, Dante Gabriel Rossetti as Designer and Writer. London: Cassell and Company, 1898. This image is in the public domain in the United States because its copyright has expired.
Pre-Raphaelite Art Exhibit, Russell Square, London, from 25 May to 25 June 1857. This was the first exhibition devoted solely to the work of the Pre-Raphaelites. Image: Portrait of Dante Gabriel Rossetti: albumen print. This photograph, from 7 October 1863, was reproduced as the frontispiece of: Rossetti, William Michael, Dante Gabriel Rossetti as Designer and Writer. London: Cassell and Company, 1898. This image is in the public domain in the United States because its copyright has expired.
 On 24 August 1857, the fall of the Ohio State Life and Trust Company in the United States marked the beginning of the 1857 financial crisis. Image: "Run on the Seamen's Savings' Bank during the Panic of 1857" by Unknown - w:Harper's Weekly available at Library of Congress. Licensed under Public Domain via Wikimedia Commons.
On 24 August 1857, the fall of the Ohio State Life and Trust Company in the United States marked the beginning of the 1857 financial crisis. Image: "Run on the Seamen's Savings' Bank during the Panic of 1857" by Unknown - w:Harper's Weekly available at Library of Congress. Licensed under Public Domain via Wikimedia Commons.
Lynn Shakinovsky, “The 1857 Financial Crisis and the Suspension of the 1844 Bank Act”
Crosby, Mark. “The Bank Restriction Act (1797) and Banknote Forgery”
Dick, Alexander J. “On the Financial Crisis, 1825-26″
Gooch, Joshua. “On ‘Black Friday,’ 11 May 1866″
 On 28 August 1857, passage of the Matrimonial Causes Act of 1857. The Act legalized divorce and protected a divorced woman’s property and future earnings. The grounds for divorce for men was adultery (in legal terms, criminal conversation), for women adultery combined with bigamy, incest, bestiality, sodomy, desertion, cruelty, or rape. Image: The Royal coat of arms of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland.
On 28 August 1857, passage of the Matrimonial Causes Act of 1857. The Act legalized divorce and protected a divorced woman’s property and future earnings. The grounds for divorce for men was adultery (in legal terms, criminal conversation), for women adultery combined with bigamy, incest, bestiality, sodomy, desertion, cruelty, or rape. Image: The Royal coat of arms of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland.
Kelly Hager, “Chipping Away at Coverture: The Matrimonial Causes Act of 1857″
Rachel Ablow, “‘One Flesh,’ One Person, and the 1870 Married Women’s Property Act”
Jill Rappoport, “Wives and Sons: Coverture, Primogeniture, and Married Women’s Property”
 On 27 October 1857, the failure of the Liverpool Borough Bank marked the beginning of the 1857 financial crisis in England. Image: "Run on the Seamen's Savings' Bank during the Panic of 1857" by Unknown - w:Harper's Weekly available at Library of Congress. Licensed under Public Domain via Wikimedia Commons.
On 27 October 1857, the failure of the Liverpool Borough Bank marked the beginning of the 1857 financial crisis in England. Image: "Run on the Seamen's Savings' Bank during the Panic of 1857" by Unknown - w:Harper's Weekly available at Library of Congress. Licensed under Public Domain via Wikimedia Commons.
Lynn Shakinovsky, “The 1857 Financial Crisis and the Suspension of the 1844 Bank Act”
Crosby, Mark. “The Bank Restriction Act (1797) and Banknote Forgery”
Dick, Alexander J. “On the Financial Crisis, 1825-26″
Gooch, Joshua. “On ‘Black Friday,’ 11 May 1866″
 March 1858 saw the first issue of England’s first feminist monthly magazine, the English Woman's Journal. Aimed primarily at a middle-class audience, the magazine promoted new employment and educational opportunities for women, and featured a mix of political and social commentary, reportage of current events, poetry, book reviews, and a correspondence column. Image: Photograph of Bessie Rayner Parkes Belloc (date unknown). This image is in the public domain in the United States because its copyright has expired.
March 1858 saw the first issue of England’s first feminist monthly magazine, the English Woman's Journal. Aimed primarily at a middle-class audience, the magazine promoted new employment and educational opportunities for women, and featured a mix of political and social commentary, reportage of current events, poetry, book reviews, and a correspondence column. Image: Photograph of Bessie Rayner Parkes Belloc (date unknown). This image is in the public domain in the United States because its copyright has expired.
Janice Schroeder, “On the English Woman’s Journal, 1858-62″
 On 24 November 1859, Charles Darwin publishes his On the Origin of Species by Means of Natural Selection. Image: Henry Maull and John Fox, Photograph of Charles Darwin (c. 1854). This image is in the public domain in the United States because its copyright has expired.
On 24 November 1859, Charles Darwin publishes his On the Origin of Species by Means of Natural Selection. Image: Henry Maull and John Fox, Photograph of Charles Darwin (c. 1854). This image is in the public domain in the United States because its copyright has expired.
Nancy Armstrong, “On Charles Darwin’s The Descent of Man, 24 February 1871″
Ian Duncan, “On Charles Darwin and the Voyage of the Beagle”
Anna Henchman, “Charles Darwin’s Final Book on Earthworms, 1881”
Martin Meisel, "On the Age of the Universe"
Cannon Schmitt, “On the Publication of Charles Darwin’s On the Origin of Species, 1859″
Daniel Bivona, “On W. K. Clifford and ‘The Ethics of Belief,’ 11 April 1876″
Goblin Market is a Victorian narrative poem written by Christina Rossetti and illustrated by her brother Dante Gabriel. Rossetti felt that the collaboration with her brother was crucial to her overall work, that she deliberately delayed the publication until Dante Garbiel’s illustrations were ready for press. He designed a total of two illustrations, the frontispiece and title page, for The Goblin Market. Both images were pressed using wood engravings, evoking the pre-raphaelite designs popular during the 1860’s. The passages appeal to the senses through vivid descriptions of colours, textures, aromas and taste. Critics assigned the poem to various general categories over the following decades and throughout the twentieth century. It was first viewed as a fairytale but was later viewed as an allegorical piece. Feminist critics often analyzed the poem’s social commentary on gender relations and the relationship between two sisters. Later in the nineteenth century, readers, reviewers, illustrators, and composers began to focus on the poem’s powerful aesthetic qualities. Its sensuous patterns, religious images, and social implications inspired the focus of school studies and as well as musical settings and performances. The power of its visual images, and the two wood-engraved designs by Dante Gabriel Rossetti in the poem’s first publication, turned to evoke numerous artistic interpretations, ranging from stained glass windows to gift books.
Curated by Kisha Rendon, Joseph Pereira, and Payton Flood
Public Domain; source: COVE Goblin Market edition by Lorraine Janzen Kooistra, Antony Harrison
by Payton Flood
In July 1866, in the aftermath of the Civil War, a permanent transatlantic cable was re-established after a failed attempt in 1858.
 On 15 August 1867, the Representation of the People Act, 1867 (also known as the Second Reform Act), received the royal assent. This act increased the electorate of England and Wales to approximately one man in three, theoretically including substantial numbers of working-class men. Image: The Royal coat of arms of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland.
On 15 August 1867, the Representation of the People Act, 1867 (also known as the Second Reform Act), received the royal assent. This act increased the electorate of England and Wales to approximately one man in three, theoretically including substantial numbers of working-class men. Image: The Royal coat of arms of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland.
Janice Carlisle, "On the Second Reform Act, 1867"
Carolyn Vellenga Berman, “On the Reform Act of 1832″
Elaine Hadley, “On Opinion Politics and the Ballot Act of 1872″
 On 26 July 1869, the Poor Rate Assessment and Collection Act, 1869, received the royal assent. This act reinstated compounding, the collection of tenants’ poor rates along with their rent, a practice that had been eliminated by the passage of the Second Reform Act Image: The Royal coat of arms of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland.
On 26 July 1869, the Poor Rate Assessment and Collection Act, 1869, received the royal assent. This act reinstated compounding, the collection of tenants’ poor rates along with their rent, a practice that had been eliminated by the passage of the Second Reform Act Image: The Royal coat of arms of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland.
Janice Carlisle, "On the Second Reform Act, 1867"
 In February 1870, passage of the Elementary Education Act Parliament provides for universal, nonsectarian education of British children at public expense and with public oversight. Image: The Royal coat of arms of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland.
In February 1870, passage of the Elementary Education Act Parliament provides for universal, nonsectarian education of British children at public expense and with public oversight. Image: The Royal coat of arms of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland.
 In April 1870, Dante Gabriel Rossetti published his first volume of original poetry, marking the start of several decades of renewed lyric experimentation by younger poets like Algernon Charles Swinburne, William Morris, Christina Rossetti, George Meredith, and Gerard Manly Hopkins. Image: Portrait of Dante Gabriel Rossetti: albumen print, 7 October 1863. This image is in the public domain in the United States because its copyright has expired.
In April 1870, Dante Gabriel Rossetti published his first volume of original poetry, marking the start of several decades of renewed lyric experimentation by younger poets like Algernon Charles Swinburne, William Morris, Christina Rossetti, George Meredith, and Gerard Manly Hopkins. Image: Portrait of Dante Gabriel Rossetti: albumen print, 7 October 1863. This image is in the public domain in the United States because its copyright has expired.
Elizabeth Helsinger, “Lyric Poetry and the Event of Poems, 1870″
 On 9 August 1870, the Married Women’s Property Act was passed. Image: The Royal coat of arms of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland.
On 9 August 1870, the Married Women’s Property Act was passed. Image: The Royal coat of arms of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland.
This Act established limited protections for some separate property for married women, including the right to retain up to £200 of any earning or inheritance. Before this all of a woman's property owned before her marriage, as well as all acquired after the marriage, automatically became her husband's alone. Only women whose families negotiated different terms in a marriage contract were able to retain control of some portion of their property.
Rachel Ablow, "On the Married Woman's Property Act, 1870"
Kelly Hager, “Chipping Away at Coverture: The Matrimonial Causes Act of 1857″
Jill Rappoport, “Wives and Sons: Coverture, Primogeniture, and Married Women’s Property”
Anne Wallace, “On the Deceased Wife’s Sister Controversy, 1835-1907″

The Irish Church Act of 1869, passed under the administration of William Gladstone (1809-1898), called for the disestablishment of the Church of Ireland. It was formally implemented on 1 January 1871. Image: Logo of the Church of Ireland, Fair use under United States copyright law
Kimberly J. Stern, "The Publication of John Pentland Mahaffy's The Decay of Modern Preaching (1882)"
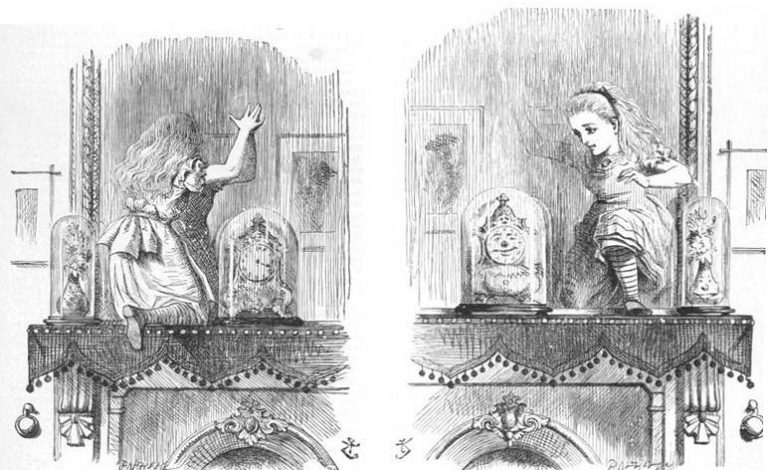 Lewis Carroll publishes Through the Looking Glass, and What Alice Found There,(1871) the sequel to Alice’s Adventures in Wonderland (1865). In this novel, Alice finds another world of nonsense and fantasy, this time by climbing through a mirror.
Lewis Carroll publishes Through the Looking Glass, and What Alice Found There,(1871) the sequel to Alice’s Adventures in Wonderland (1865). In this novel, Alice finds another world of nonsense and fantasy, this time by climbing through a mirror.
Jean Little, “Algebraic Logic in Through the Looking Glass”
 September 1873 saw the beginning of the "panic of 1873," a financial crisis brought on in part by speculation in railroads. The crisis included the fall of American banking house Jay Cook & Company, which was precipitated by the failure of Northern Pacific Railway shares. The panic triggered a depression in Europe and North America that lasted from 1873 until 1879. Image: Portrait, Jay Cooke, founder of Jay Cooke & Company. This image is in the public domain in the United States as its copyright has expired.
September 1873 saw the beginning of the "panic of 1873," a financial crisis brought on in part by speculation in railroads. The crisis included the fall of American banking house Jay Cook & Company, which was precipitated by the failure of Northern Pacific Railway shares. The panic triggered a depression in Europe and North America that lasted from 1873 until 1879. Image: Portrait, Jay Cooke, founder of Jay Cooke & Company. This image is in the public domain in the United States as its copyright has expired.
Joshua Gooch, “On ‘Black Friday,’ 11 May 1866″
 The Second Anglo-Afghan War grew out of longstanding tensions between Russia and Britain over Britain’s prized colonial possession of India. It lasted from November 1878 to May 1881. Image: Battle of Kandahar, 1880, by W. Skeoch Cumming. This image is in the public domain in the United States because its copyright has expired.
The Second Anglo-Afghan War grew out of longstanding tensions between Russia and Britain over Britain’s prized colonial possession of India. It lasted from November 1878 to May 1881. Image: Battle of Kandahar, 1880, by W. Skeoch Cumming. This image is in the public domain in the United States because its copyright has expired.
Zarena Aslami, “The Second Anglo-Afghan War, or The Return of the Uninvited”
Antoinette Burton, “On the First Anglo-Afghan War, 1839-42: Spectacle of Disaster”
In January 1880, a four-day fog event in London killed some 1,100 people. Image. Photograph of Widnes (north west England in the late nineteenth century, from D. W. F. Hardie, A History of the Chemical Industry in Widnes. 1950. Courtesy of Wikimedia Commons:upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia….
 1882 Married Women's Property Act passed on 1 Jan 1883. Referred to as the 1882 MWPA, the Act came into effect at the beginning of 1883. Although still identifying some married women's property as "separate," this Act significantly increased the scope and protections for married women's acquisition and retention of property separate from their husbands. Image: The Royal coat of arms of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland.
1882 Married Women's Property Act passed on 1 Jan 1883. Referred to as the 1882 MWPA, the Act came into effect at the beginning of 1883. Although still identifying some married women's property as "separate," this Act significantly increased the scope and protections for married women's acquisition and retention of property separate from their husbands. Image: The Royal coat of arms of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland.
Jill Rappoport, “Wives and Sons: Coverture, Primogeniture, and Married Women’s Property”
Anne Wallace, “On the Deceased Wife’s Sister Controversy, 1835-1907″
Rachel Ablow, “‘One Flesh,’ One Person, and the 1870 Married Women’s Property Act”
 Criminal Law Amendment Act passed on 14 August 1885. The Act raised the age of consent for girls from 13 to 16 and introduced the misdemeanor of “gross indecency” to criminalize sexual acts between men in public or private. Image: The Royal coat of arms of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland.
Criminal Law Amendment Act passed on 14 August 1885. The Act raised the age of consent for girls from 13 to 16 and introduced the misdemeanor of “gross indecency” to criminalize sexual acts between men in public or private. Image: The Royal coat of arms of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland.
Mary Jean Corbett, “On Crawford v. Crawford and Dilke, 1886″
Andrew Elfenbein, “On the Trials of Oscar Wilde: Myths and Realities”
 The 1887 Year of Jubilee was a celebration of the fiftieth anniversary of the reign of Queen Victoria. Image: George Hayter, State portrait of Queen Victoria, 1860 (oil on canvas), from the Government Art Collection of the United Kingdom. This image is in the public domain in the United States because its copyright has expired.
The 1887 Year of Jubilee was a celebration of the fiftieth anniversary of the reign of Queen Victoria. Image: George Hayter, State portrait of Queen Victoria, 1860 (oil on canvas), from the Government Art Collection of the United Kingdom. This image is in the public domain in the United States because its copyright has expired.
Erika Rappaport, “Object Lessons and Colonial Histories: Inventing the Jubilee of Indian Tea”
 On 13 November 1887, “Bloody Sunday” occurred. Police charged against socialists after a Trafalgar Square protest against unemployment and the Irish Coercion Acts; 75 were wounded. At another Trafalgar Square protest on November 20, a bystander, Alfred Linnell, was trampled by a police horse and later died of wounds. Image: Bloody Sunday, 1887. This engraving from the The Illustrated London News depicts a policeman being clubbed by a demonstrator as he wrests a banner from a female protester.
On 13 November 1887, “Bloody Sunday” occurred. Police charged against socialists after a Trafalgar Square protest against unemployment and the Irish Coercion Acts; 75 were wounded. At another Trafalgar Square protest on November 20, a bystander, Alfred Linnell, was trampled by a police horse and later died of wounds. Image: Bloody Sunday, 1887. This engraving from the The Illustrated London News depicts a policeman being clubbed by a demonstrator as he wrests a banner from a female protester.
Florence Boos, “The Socialist League, founded 30 December 1884″
In July 1888, the London Matchgirls' Strike occurred.
Heidi Kaufman, “1800-1900: Inside and Outside the Nineteenth-Century East End”
From August 1888 to September 1889, the serial killer known as the Whitechapel Murderer or Jack the Ripper stalked women living in the East End of London.
Heidi Kaufman, “1800-1900: Inside and Outside the Nineteenth-Century East End”
The Yellow Peril was a term originated in Imperial Germany in the 1890s. This term was a color-metaphor referred to Western fears that Asians, particularly the Chinese, would invade their lands and disrupt Western values, such as democracy, Christianity, and technological innovation. The term of the Yellow Peril spread through Britain with the rise of Chinese populations in the aftermath of the Boxer Rebellion (Nov 2, 1899 – Sep 7, 1901). The Boxer Rebellion was an uprising movement against foreigners that occurred at the end of the Qing dynasty in northern China. The Boxer did experienced suppression by allied forces in China; however, the Western anxieties continually increased, which turned into the fears of the “Yellow Peril”. The most recognizable character of “Yellow Peril” was Dr. Fu Manchu, a villain from the series of novels written by a British author Sax Rohmer. Image: A 1913 cover of Sax Rohmer’s The Mystery of Dr. Fu-Macnhu
Articles:
by Shiqi Deng
 In January 1892, Charlotte Perkins Gilman published her semi-autobiographical short story, “The Yellow Wallpaper,” in the New England Magazine. The tale’s heroine is a depressed new mother who goes mad while enduring a modified Rest Cure. Gilman herself underwent the Rest Cure in 1887 at the hands of Philadelphia neurologist Silas Weir Mitchell, who is briefly mentioned in the story. Image: Photograph of Silas Weir Mitchell, 1881. This image is in the public domain in the United States because its copyright has expired.
In January 1892, Charlotte Perkins Gilman published her semi-autobiographical short story, “The Yellow Wallpaper,” in the New England Magazine. The tale’s heroine is a depressed new mother who goes mad while enduring a modified Rest Cure. Gilman herself underwent the Rest Cure in 1887 at the hands of Philadelphia neurologist Silas Weir Mitchell, who is briefly mentioned in the story. Image: Photograph of Silas Weir Mitchell, 1881. This image is in the public domain in the United States because its copyright has expired.
Anne Stiles, “The Rest Cure, 1873-1925″
 On 6 October 1892, the Poet Laureate, Alfred, Lord Tennyson, died, beginning a heated debate about who should succeed him as Poet Laureate. Image: Julia Margaret Cameron, Carbon print of Alfred Lord Tennyson, 1869, printed 1875/79 (The Art Institute of Chicago). This image is in the public domain in the United States because its copyright has expired.
On 6 October 1892, the Poet Laureate, Alfred, Lord Tennyson, died, beginning a heated debate about who should succeed him as Poet Laureate. Image: Julia Margaret Cameron, Carbon print of Alfred Lord Tennyson, 1869, printed 1875/79 (The Art Institute of Chicago). This image is in the public domain in the United States because its copyright has expired.
Linda Peterson, “On the Appointment of the ‘Poet Laureate to Her Majesty,’ 1892-1896”
In March 1894, Sarah Grand's “The New Aspect of the Woman Question” was published. The essay in North American Review, vol.158, no.448, March 1894, pp.270–6 has been credited with identifying the "New Woman."
Meaghan Clarke, “1894: The Year of the New Woman Art Critic”
 On 27 June 1894, Mudie’s Select Library and W. H. Smith’s, the largest of the private circulating libraries that provided many Victorians with their reading material, issued simultaneous announcements specifying the new terms on which they would buy novels from publishers, beginning in the next calendar year. This change spelled the effective end of the 3-volume system; whereas 112 three-volume works were published in 1894, only two were published in 1897. Image: "Going to Mudie's," London Society v.16, no. 95, Nov. 1869. This image is in the public domain in the United States as its copyright has expired.
On 27 June 1894, Mudie’s Select Library and W. H. Smith’s, the largest of the private circulating libraries that provided many Victorians with their reading material, issued simultaneous announcements specifying the new terms on which they would buy novels from publishers, beginning in the next calendar year. This change spelled the effective end of the 3-volume system; whereas 112 three-volume works were published in 1894, only two were published in 1897. Image: "Going to Mudie's," London Society v.16, no. 95, Nov. 1869. This image is in the public domain in the United States as its copyright has expired.
Richard Menke, “The End of the Three-Volume Novel System, 27 June 1894″
 The trials of Oscar Wilde, which occurred in April and May of 1895, have become legendary as a turning-point in the history of public awareness of homosexuality. By their close, Wilde had gone from being a triumphantly successful playwright to a ruined man, condemned to two years of hard labor for gross indecency. They garnered extensive coverage first in the London press and then in newspapers around the world; the story of the trials continues to be retold in ways that have persistent relevance for contemporary queer culture. Image: Photograph of Oscar Wilde, by Napoleon Sarony. This image is in the public domain in the United States because its copyright has expired.
The trials of Oscar Wilde, which occurred in April and May of 1895, have become legendary as a turning-point in the history of public awareness of homosexuality. By their close, Wilde had gone from being a triumphantly successful playwright to a ruined man, condemned to two years of hard labor for gross indecency. They garnered extensive coverage first in the London press and then in newspapers around the world; the story of the trials continues to be retold in ways that have persistent relevance for contemporary queer culture. Image: Photograph of Oscar Wilde, by Napoleon Sarony. This image is in the public domain in the United States because its copyright has expired.
Andrew Elfenbein, “On the Trials of Oscar Wilde: Myths and Realities”
 On 11 Oct 1899, war was declared between Britain and the Transvaal Republic and Orange Free State, two independent Boer nations in southern Africa. The Treaty of Vereeniging concluded the Second Boer War on 31 May 1902. The fighting had resulted in c. 45,000 British military casualties and around 40,000 combined military and civilian casualties among the Boers. Eight years later in 1910, the Union of South Africa made the region a dominion of the British Empire. Image: Walter Crane, “Stop the War,” page 297, The War Against War in South Africa, 23 February 1900, wood engraving, courtesy of Yale University.
On 11 Oct 1899, war was declared between Britain and the Transvaal Republic and Orange Free State, two independent Boer nations in southern Africa. The Treaty of Vereeniging concluded the Second Boer War on 31 May 1902. The fighting had resulted in c. 45,000 British military casualties and around 40,000 combined military and civilian casualties among the Boers. Eight years later in 1910, the Union of South Africa made the region a dominion of the British Empire. Image: Walter Crane, “Stop the War,” page 297, The War Against War in South Africa, 23 February 1900, wood engraving, courtesy of Yale University.
Jo Briggs, “The Second Boer War, 1899-1902: Anti-Imperialism and European Visual Culture”
 4 April 1906 saw the royal assent to the Aborigines Act 1905 (5 Edw. VII No. 14), in which Section 70 (which sought to protect and support the welfare of Aboriginal people) was repealed for a second time. Image: Coat of Arms of Australia. This image is in the public domain in the United States as its copyright has expired.
4 April 1906 saw the royal assent to the Aborigines Act 1905 (5 Edw. VII No. 14), in which Section 70 (which sought to protect and support the welfare of Aboriginal people) was repealed for a second time. Image: Coat of Arms of Australia. This image is in the public domain in the United States as its copyright has expired.
|
Date |
Event | Created by | Associated Places | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 28 May 1836 |
Elizabeth Barrett Browning dinner with WordsworthOn 28 May 1836, Elizabeth Barrett Browning met William Wordsworth at a literary dinner in London; EBB's cousin, John Kenyon, was the host and the event most likely occurred at Kenyon's main residence at the time: 39 Devonshire Place, London, which is right around the corner from EBB's residence at the time: 50 Wimpole Street. See the associated map. |
Dino Franco Felluga | ||
| 29 Aug 1833 |
Slavery Abolition Act
Articles |
David Rettenmaier | ||
| 29 Aug 1833 |
Factory Act
ArticlesRelated Articles |
David Rettenmaier | ||
| Oct 1831 to Oct 1836 |
Darwin's voyage on the Beagle
ArticlesNancy Armstrong, “On Charles Darwin’s The Descent of Man, 24 February 1871″ Ian Duncan, “On Charles Darwin and the Voyage of the Beagle” Anna Henchman, “Charles Darwin’s Final Book on Earthworms, 1881” Cannon Schmitt, “On the Publication of Charles Darwin’s On the Origin of Species, 1859″ Related ArticlesDaniel Bivona, “On W. K. Clifford and ‘The Ethics of Belief,’ 11 April 1876″ |
David Rettenmaier | ||
| Sep 1831 to Dec 1832 |
Cholera EpidemicThe first major cholera pandemic to cross the Channel began in Sunderland in September 1831, spread throughout the country, and was not determined to be over until more than a year later, in December of 1832. Articles |
David Rettenmaier | ||
| 1831 |
A History of Mary PrinceStory by Mary Prince, transcribed by Suzanna Strickland, edited by Thomas Pringle |
Stacey Kikendall | ||
| 15 Sep 1830 |
Opening of Liverpool & Manchester Railway
Articles
|
David Rettenmaier | ||
| Aug 1830 to Dec 1830 |
Swing Riots
Related ArticlesCarolyn Lesjak, "1750 to the Present: Acts of Enclosure and Their Afterlife" (forthcoming) |
David Rettenmaier | ||
| 26 Jun 1830 |
Death of King George IV
Related Articles |
David Rettenmaier | ||
| 1 Jan 1830 |
Principles of Geology
Lyell’s work, though contested, establishes the preeminence of Uniformitarian principles in the interpretation of Geological phenomena, and allows vast temporal scope for Charles Darwin’s subsequent model of evolutionary development. ArticlesMartin Meisel, "On the Age of the Universe" Related ArticlesNancy Armstrong, “On Charles Darwin’s The Descent of Man, 24 February 1871″ Ian Duncan, “On Charles Darwin and the Voyage of the Beagle” Anna Henchman, “Charles Darwin’s Final Book on Earthworms, 1881” Cannon Schmitt, “On the Publication of Charles Darwin’s On the Origin of Species, 1859″ |
David Rettenmaier | ||
| 1830 |
Death of George IV, William IV becomes KingBrother of George IV, son of George III |
Stacey Kikendall | ||
| 1 Apr 1829 |
Roman Catholic Relief Act
The Catholic Relief Act of 1829 allowed Catholics to become Members of Parliament and to hold public offices, but it also raised the property qualifications that allowed individuals in Ireland to vote. The passage of the Catholic Relief Act marked a shift in English political power from the House of Lords to the House of Commons. The Act was led by the Duke of Wellington and passed despite initially serious opposition from both the House of Lords and King George IV. ArticlesRelated ArticlesCarolyn Vellenga Berman, “On the Reform Act of 1832″ Sean Grass, “On the Death of the Duke of Wellington, 14 September 1852″ |
David Rettenmaier | ||
| 1828 |
Test Act RepealedParliamentary repeal of the Test and Corporation Acts excluding Dissenters from state offices |
Stacey Kikendall | ||
| Dec 1825 |
Bank failures in London
ArticlesAlexander J. Dick, “On the Financial Crisis, 1825-26″ Related ArticlesAngela Esterhammer, “1824: Improvisation, Speculation, and Identity-Construction” Lana L. Dalley, “On Martineau’s Illustrations of Political Economy, 1832-34″ |
David Rettenmaier | ||
| Apr 1825 |
Stock market crashOn April 1825, the British stock market began to crash. After the speculative bubble reached its peak, falling Bank of England gold reserves and a collapse in stock prices lead to panic by the end of the year. Related ArticlesAngela Esterhammer, “1824: Improvisation, Speculation, and Identity-Construction” |
David Rettenmaier | ||
| 16 Jun 1824 |
Society for Protection of Animals foundedOn 16 June 1824, founding of the Society for the Protection of Animals (SPCA) in London. The Society became the Royal Society in 1840, when it was granted a royal charter by Queen Victoria, herself strongly opposed to vivisection. ArticlesRelated ArticlesSusan Hamilton (U Alberta), “On the Cruelty to Animals Act, 15 August 1876″ Philip Howell, “June 1859/December 1860: The Dog Show and the Dogs’ Home” Mario Ortiz-Robles, “Animal Acts: 1822, 1835, 1849, 1850, 1854, 1876, 1900″ |
David Rettenmaier | ||
| 5 May 1821 |
Death of NapoleonNapoleon Bonaparte died on 5 May 1821 while in Exile on the island of Saint Helena. Image: Horace Vernet, Napoleon on his Death Bed (1826). |
Dino Franco Felluga | ||
| 1820 |
Ode on a Grecian UrnWritten by John Keats |
Stacey Kikendall | ||
| 1820 |
George IV becomes KingAfter serving as Regent for years, he eventually becomes King when his father dies. |
Stacey Kikendall | ||
| 30 Dec 1819 |
Gag Acts
Articles |
David Rettenmaier | ||
| 15 Nov 1819 |
Simultaneous Scottish radical meetingsOn 15 November 1819, simultaneous radical meetings occurred at Paisley, Glasgow, and other locations across Scotland. Articles |
David Rettenmaier | ||
| 1 Nov 1819 |
Simultaneous radical meetingsOn 1 November 1819, simultaneous meetings were held, by prior agreement, at Newcastle, Carlisle, Leeds Halifax, Manchester, Bolton, Nottingham, Leicester, Coventry, and elsewhere in England and Scotland. Articles |
David Rettenmaier | ||
| 16 Aug 1819 |
Peterloo massacre
Related ArticlesJames Chandler, “On Peterloo, 16 August 1819″ Sean Grass, “On the Death of the Duke of Wellington, 14 September 1852″ |
David Rettenmaier | ||
| 12 Jul 1819 |
Britain approves settlement scheme to South AfricaOn 12 July 1819, the British government approved £50,000 for a settlement scheme to South Africa's eastern Cape. Articles |
David Rettenmaier | ||
| 26 Sep 1818 |
First medical blood transfusion between humans
ArticlesMatthew Rowlinson, “On the First Medical Blood Transfusion Between Human Subjects, 1818″ |
David Rettenmaier | ||
| 1 Apr 1817 |
First number of Blackwood's Edinburgh Magazine
ArticlesMichelle Allen-Emerson, “On Magazine Day” Related Articles |
David Rettenmaier | ||
| Dec 1815 |
Emma
ArticlesAnne Wallace, “On the Deceased Wife’s Sister Controversy, 1835-1907″ |
David Rettenmaier | ||
| 2 Mar 1815 |
Corn Law Act
The Corn Law Act of 1815 prohibited the importation of grain when the prices in the domestic market were high. The Act was repealed on 25 June 1846. Articles |
David Rettenmaier | ||
| 6 Apr 1814 to 26 Feb 1815 |
Napoleon exiled to ElbaNapoleon was exiled to Elba, an island in the Meditteranean, after he abdicated on 6 April 1814. He spent nine months and 21 days on the island, then attempted to retake his empire, leaving the island on 26 February 1815. Napoleon was definitively defeated at the Battle of Waterloo on 18 June 1815. |
Dino Franco Felluga | ||
| 1813 |
Pride and PrejudiceWritten by Jane Austen |
Stacey Kikendall | ||
| 1812 to 1815 |
1812 WarWar between Britain and United States |
Stacey Kikendall | ||
| 16 Oct 1811 |
National Society for the Education of Poor Children foundedOn 16 October 1811, the National Society for the Education of Poor Children in the Principles of the Established Church (the Church of England) was founded to establish “National Schools.” According to their founders, poor children were to be taught to avoid vice and behave in an orderly manner within their station. To limit costs, the monitorial system was employed, by which more advanced pupils taught younger ones. Related ArticlesFlorence S. Boos, “The Education Act of 1870: Before and After” |
David Rettenmaier | ||
| 1811 to 1820 |
The RegencyGeorge, Prince of Wales, acts as regent for George III, who has been declared incurably insane |
Stacey Kikendall | ||
| 1807 |
British slave trade outlawedSlave trade outlawed (but not slavery itself) |
Stacey Kikendall | ||
| 26 May 1805 |
Napoleon made king of Italy
In a flamboyant and highly theatrical gesture, Napoleon Bonaparte signifies his political and military dominance over the Italian peninsula with a ceremony in Milan Cathedral, where he crowned himself King of Italy with the ancient, iconic iron crown of Lombardy. This crowning of Napoleon as King is a result of the French conquest of Italy. His full title was "Emperor of the French and King of Italy." ArticlesAlison Chapman, "On Il Risorgimento" Related Articles |
David Rettenmaier | ||
| 1802 |
William Wordsworth's Lyrical BalladsWilliam Wordsworth's Lyrical Ballads, 3rd edition, containing the expanded and final version of the famous "Preface," one of the founding theoretical statements of the Romantic poetical movement. This image is in the public domain in the United States because its copyright is expired. https://www.abebooks.com/first-edition/Lyrical-Ballads-Pastoral-Poems-Vo... Articles |
David Rettenmaier | ||
| Jan 1801 |
Inclosure Act
ArticlesCarolyn Lesjak, "1750 to the Present: Acts of Enclosure and Their Afterlife" (forthcoming) |
David Rettenmaier | ||
| 1801 |
1801 Ireland joins Great BritainParliamentary Union of Ireland and Great Britain. Act of Union passed in 1800, took effect in 1801 |
Stacey Kikendall | ||
| 1798 |
Rebellion in IrelandUprising against British rule in Ireland, had help of French but were eventually defeated |
Stacey Kikendall | ||
| 1794 |
Songs of Innocence and of ExperienceWritten by William Blake The Songs of Innocence was originally etched in 1789, but was combined with additional poems in 1794 as Songs of Innocence and of Experience |
Stacey Kikendall | ||
| 5 Sep 1793 to 27 Jul 1794 |
Reign of Terror
On 5 September 1793, the National Convention, France’s ruling body from 1793 to 1795, officially put into effect terror measures in order to subdue opposition to and punish insufficient support for the revolution and the new regime. From the autumn of 1793 until the summer of 1794, thousands of people across the country were imprisoned and executed (including the Queen) under the ruthless leadership of Maximilien Robespierre. The guillotine, particularly the one in Paris’s Place de la Révolution, served as the bloody emblem of the fear tactics that began to manifest themselves first in the formation of the Committee of Public Safety (6 April 1793) and subsequently in the implementation of the Law of Suspects (17 September 1793). The Terror ended on 27 July 1794 with the overthrow of Robespierre, who was guillotined the next day. ArticlesDiane Piccitto, "On 1793 and the Aftermath of the French Revolution" |
David Rettenmaier | ||
| 1 Jan 1792 |
Vindication of the Rights of Woman
ArticlesAnne K. Mellor, "On the Publication of A Vindication of the Rights of Woman" Related Articles |
David Rettenmaier | ||
| 1791 |
Epistle to William Wilberforce, Esq. on the Rejection of the Bill for Abolishing the Slave TradeWritten by Anna Letitia Barbauld |
Stacey Kikendall | ||
| 5 May 1789 to 10 Nov 1799 |
French Revolution
On 5 May 1789, the Estates-General, representing the nobility, the clergy, and the common people, held a meeting at the request of the King to address France’s financial difficulties. At this meeting, the Third Estate (the commoners) protested the merely symbolic double representation that they had been granted by the King. This protest resulted in a fracture among the three estates and precipitated the French Revolution. On 17 June, members of the Third Estate designated themselves the National Assembly and claimed to represent the people of the nation, thus preparing the way for the foundation of the republic. Several pivotal events followed in quick succession: the storming of the Bastille (14 July), the approval of the Declaration of the Rights of Man and of the Citizen (26 August), and the march on Versailles that led to the enforced relocation of the royal family to Paris (5-6 October). These revolutionary acts fired the imagination of many regarding the political future of France, and, indeed, all of Europe. The republican period of the revolution continued in various phases until 9-10 November 1799 when Napoleon Bonaparte supplanted the government. ArticlesDiane Piccitto, "On 1793 and the Aftermath of the French Revolution" |
David Rettenmaier | ||
| Jan 1789 |
Interesting Narrative of the Life of Olaudah Equiano
Articles |
David Rettenmaier | ||
| 1789 |
Written in the Church-Yard at Middleton in SussexWritten by Charlotte Smith, included in her collection Elegiac Sonnets |
Stacey Kikendall | ||
| 9 Apr 1787 |
First settlers depart for Sierra Leone
Articles |
David Rettenmaier | ||
| May 1781 |
Sunday Observance Act
Passage of this Act, formally titled “Act for Preventing Certain Abuses and Profanations on the Lord’s Day, Called Sunday,” had a powerful, repressive effect on British society and culture for more than a century-and-a-half, as noted by both its proponent (Bishop Beilby Porteus) and its many Victorian critics, among them John Stuart Mill in On Liberty. ArticlesChristopher Lane, "On the Victorian Afterlife of the 1781 Sunday Observance Act" |
David Rettenmaier | ||
| 1775 to 1783 |
American RevolutionAmerican colonies rebel against British rule |
Stacey Kikendall | ||
| 1773 |
A Mouse's PetitionWritten by Anna Letitia Barbauld around 1771, published in 1773 |
Stacey Kikendall |